December 21 is a Solstice Day in 2010link
The December solstice will occur at 23:38 (or 11.38pm) Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) on December 21, 2010. It is also known as the winter solstice in the northern hemisphere and the summer solstice in the southern hemisphere due to the seasonal differences. Its date varies from December 20 to December 23 depending on the year in the Gregorian calendar.To find the December solstice date in other time zones or other years, please use the Seasons Calculator.
The December Solstice Explained
The December solstice occurs when the sun reaches its most southerly declination of -23.5 degrees. In other words, it is when the North Pole is tilted 23.5 degrees away from the sun. Depending on the Gregorian calendar, the December solstice occurs annually on a day between December 20 and December 23. On this date, all places above a latitude of 66.5 degrees north are now in darkness, while locations below a latitude of 66.5 degrees south receive 24 hours of daylight.The sun is directly overhead on the Tropic of Capricorn in the southern hemisphere during the December solstice. It also marks the longest day of the year in terms of daylight hours for those living south of the Tropic of Capricorn. Those living or travelling south from the Antarctic Circle towards the South Pole will see the midnight sun during this time of the year.
On the contrary, for an observer in the northern hemisphere, the December solstice marks the day of the year with the least hours of daylight for those living north of the Tropic of Cancer. Those living or traveling north of the Arctic Circle towards the North Pole will not be able to see the sun during this time of the year.
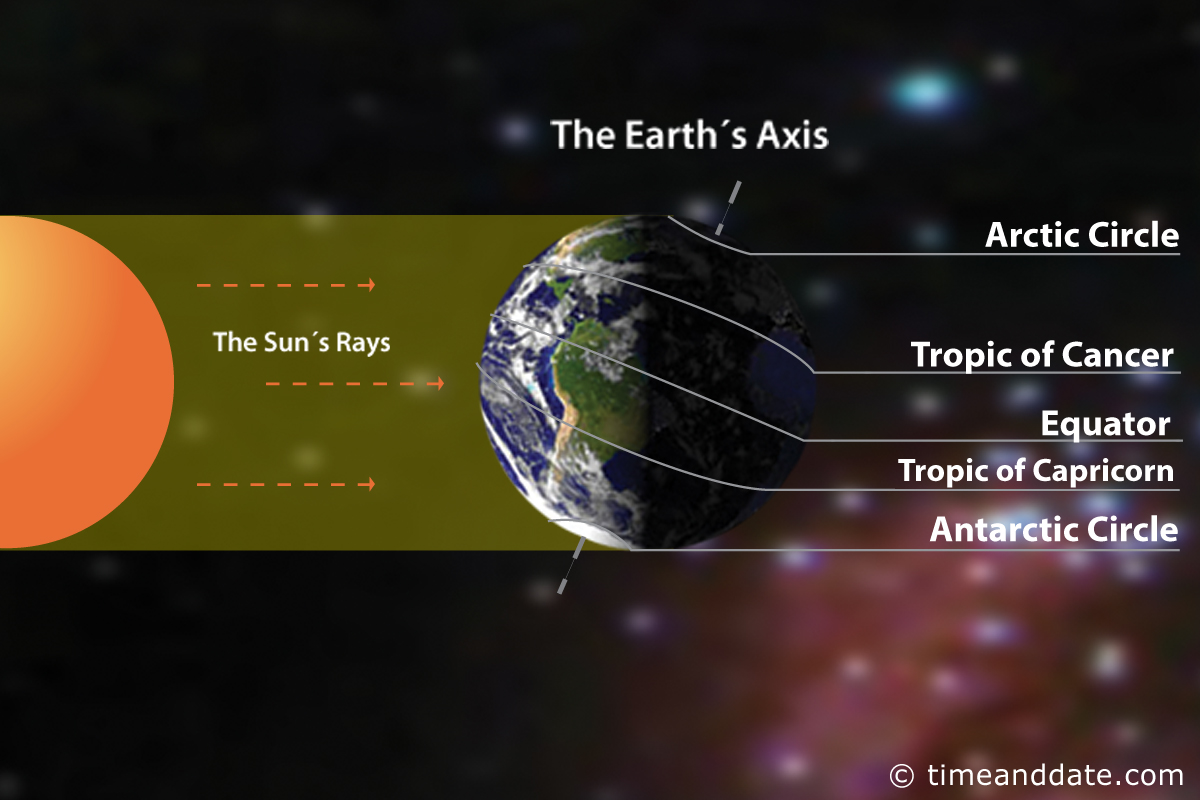
Illustration is not to scale
The December solstice in the calendar
December 20 and December 23 solstices occur less frequently than December 21 or December 22 solstices in the Gregorian calendar. The last December 23 solstice occurred in 1903 and will not occur again until the year 2303. A December 20 solstice has occurred very rarely, with the next one occurring in the year 2080.As with the June solstice, the December solstice’s varying dates are mainly due to the calendar system. The Gregorian calendar, which is used in most western countries, has 365 days in a year and 366 days in a leap year. However, the tropical year, which is the length of time the sun takes to return to the same position in the seasons cycle (as seen from earth), is different to the calendar year. The tropical year is approximately 365.242199 days but varies from year to year because of the influence of other planets. The exact orbital and daily rotational motion of the earth, such as the “wobble” in the earth's axis (precession), also contributes to the changing solstice dates.
Over the course of history, many different schemes have been devised to determine the start of the year. Some are astronomical, beginning at the September or March equinox, or at the June or December solstice. Solstices are more readily observable either by observing when the midday shadow of a gnomon is longest (winter solstice in the northern hemisphere) or shortest (summer solstice in the northern hemisphere). The solstices can also be observed by noting the point of time when the sun rises or sets as far south as it does during the course of the year (winter in the northern hemisphere) or maximally north (summer in the northern hemisphere).
December solstice in relation to seasons
It is important to note that earth does not move at a constant speed in its elliptical orbit. Therefore the seasons are not of equal length: the times taken for the sun to move from the vernal equinox to the summer solstice, to the autumnal equinox, to the winter solstice, and back to the vernal equinox are roughly 92.8, 93.6, 89.8 and 89.0 days respectively. The consolation in the northern hemisphere is that spring and summer last longer than autumn and winter (when the December solstice occurs).The relative position of the earth's axis to the sun changes during the cycle of seasons. This phenomenon is the reason why the sun’s height above the horizon changes throughout the year. It is also responsible for the seasons through controlling the intensity and duration of sunlight received at various locations around the planet.
No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: only a member of this blog may post a comment.